Create or Update Connections
Connection Parameters
Connection name
Required.
Free form name of the connection. For better navigation, the connection name might include name of the database server, the connection user name, default database or schema.
Connection description
Connection description might have additional information about the connection. For example, the connection owner, permissions assigned to the database user, password expiration date and any other.
Database type
Required.
Type of the database connection.
Currently supported types are
| Type | Version | Supported |
|---|---|---|
| Oracle | 10g and later | Yes |
| PostgreSQL | 9.3 and later | Yes |
JDBC URL
Required.
The format of the URL depends on the database type selected. You can find detailed description of the available options in the database vendor documents.
Oracle
By Service Name
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<host>:<port, 1521>/<Service name>
By SID
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//<host>:<port, 1521>:<SID>
By TNS
jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)
(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host1)(PORT=5221))
(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host2)(PORT=5221)))
(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=orcl)))
See more in JDBC Developer's Guide.
PostgreSQL
jdbc:postgresql://<host>:<port, 5432>/database
See more in Connecting to the Database.
Scheme
Default scheme that the connection use to access tables in the source or target database.
You can override the scheme in the post-connection script or leave it empty to use database default schema name.
For example, in Oracle the post script might look
alter session set current_schema = "my.special.scheme"
If scheme enclosed in double quotes, the name will be used as is. Such names can have special, national, and case sensitive characters or special words. Nevertheless, this is not recommended and might cause issues access such tables with various tools that does not support the feature.
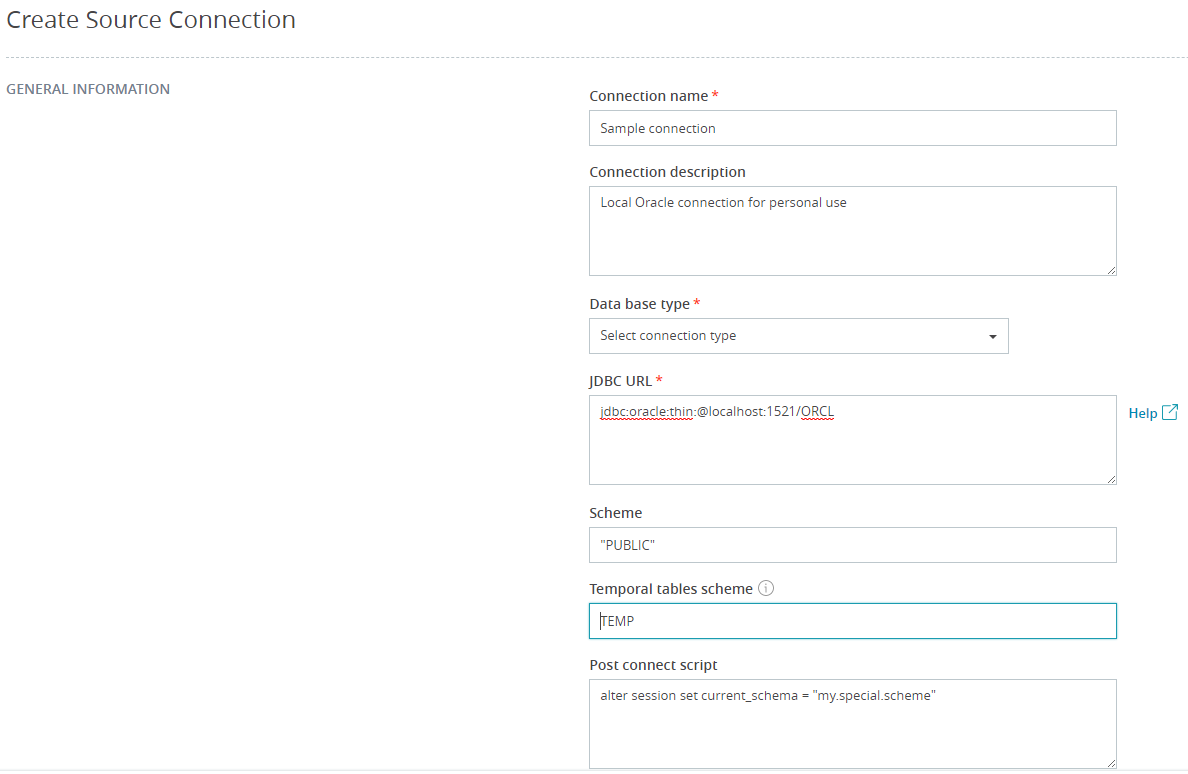
Temporal tables scheme (source connections only)
Name of the database schema the connection user has permissions to create and drop tables, insert rows into the created tables. The connection will be marked as "Limited" if the user has no such permissions.
We use temporal tables to:
- Collect IDs of records to copy
- Optimize access delays to the source data
- Minimize the volume of data to transfer between database and the Spark cluster.
The schema should have enough space to store the intermediate results that can take roughly 10% of the data volume to transfer.
If the value is not set, user's default schema will be used for temporal tables creation.
The user should have at least following permissions:
- Create and Alter a table in the schema for temporal tables
- Insert records into the tables
- Drop the tables.
If you don't specify the temporal schema name, we will use default schema for the connection user. The post connect script does not affect the temporal schema.
Post connect script
We will execute the script as the last step to establish the connection. We strongly recommend to keep it as small and light as possible. We cannot predict how many times we will execute the script.
You can use it to fine-tune database session parameters, setting default date and time formats, or changing default schema.
You can add few SQL statements in one script. The statements must start from the new line and end with semicolon (;).
alter session set current_schema = "my.special.scheme";
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_LANGUAGE= 'AMERICAN'
NLS_TERRITORY= 'AMERICA'
NLS_CURRENCY= '$'
NLS_ISO_CURRENCY= 'AMERICA'
NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS= '.,'
NLS_CALENDAR= 'GREGORIAN'
NLS_DATE_FORMAT= 'DD-MON-RR'
NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE= 'AMERICAN'
NLS_SORT= 'BINARY';
Proxy
TBD
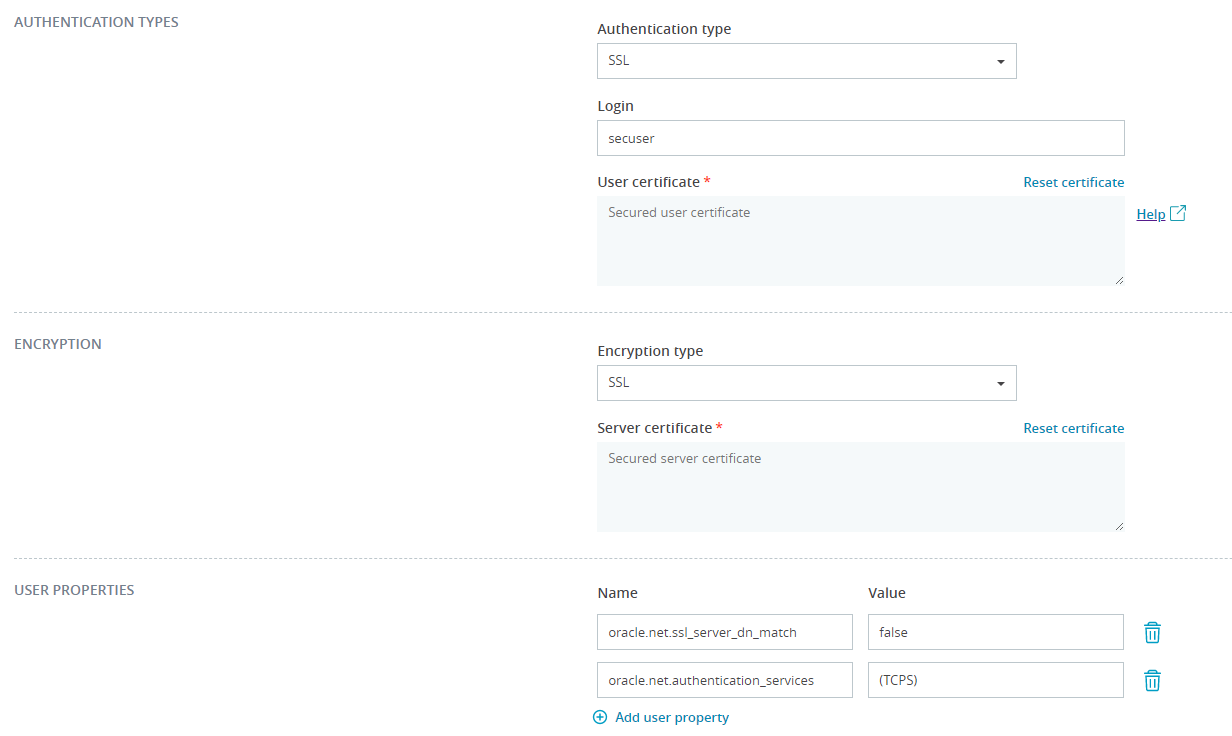
Authentication type
Basic
User authenticated with combination of the user name and password fields.
SSL
The SSL Authentication method for Oracle and PostgreSQL connections require the SSL encryption enabled and a valid server certificate provided.
You can authenticate in the source or target database using trusted certificate. We store the certificate along with the connection and send it to Spark cluster in the password protected Java Key Store format (JKS).
The connection configuration page accepts user certificate chains in the X.509 and user certificate chains in the RSA (PKCS#8) formats:
Bag Attributes
localKeyID: 27 C4 A6 71 C6 94 4C FF 0C 8D DD 37 5C 83 D2 F6 5B 88 F6 5E
subject=/C=US/ST=secuser/L=secuser/O=secuser/OU=secuser/CN=secuser
issuer=/C=US/ST=rootCA/L=rootCA/O=rootCA/OU=rootCA/CN=rootCA
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDRTCCAi0CCQDQpKNLZxPVOzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADBiMQswCQYDVQQGEwJV
UzEPMA0GA1UECAwGcm9vdENBMQ8wDQYDVQQHDAZyb290Q0ExDzANBgNVBAoMBnJv
...
v5Am9XNvKVPwTEWsiAh+19gahw6waNnQ9shy+U+1q03HO2CEXIFpyp4KsMwVGG56
p6Bu1Ibwcj+KBZtc6f1knOuTP/AveCTYTA==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
Bag Attributes: <No Attributes>
subject=/C=US/ST=rootCA/L=rootCA/O=rootCA/OU=rootCA/CN=rootCA
issuer=/C=US/ST=rootCA/L=rootCA/O=rootCA/OU=rootCA/CN=rootCA
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDlzCCAn+gAwIBAgIJAOc2bAZ4pWEPMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMGIxCzAJBgNV
BAYTAlVTMQ8wDQYDVQQIDAZyb290Q0ExDzANBgNVBAcMBnJvb3RDQTEPMA0GA1UE
...
nCuzEFBF6RY6+LA=
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
Bag Attributes
localKeyID: 27 C4 A6 71 C6 94 4C FF 0C 8D DD 37 5C 83 D2 F6 5B 88 F6 5E
Key Attributes: <No Attributes>
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIEvQIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAASCBKcwggSjAgEAAoIBAQClMVwNTVsrXR6G
iLNrAyEUbbTLbIz/ZQLgpodhUOYi+mgvPchq0FsAvUYS4yQIClTgA8XnEcvXl+ky
...
9No9g3zefukCsbdDwo5HocxSWvGsBMFK9NqY24KI1LooacGStRJ7A0ivnudYkYcu
4BYENOv+U9N8B8I0UXkX0Mc=
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
Oracle SSL authentication requires additional connection parameters. At least the authentication service must be specified, for example
oracle.net.authentication_services=(TCPS)
If you mix fully qualified domain names and short server name make sure you disable DN matching
oracle.net.ssl_server_dn_match=false
See more in Oracle - Configuring Secure Sockets Layer Authentication.
PostgreSQL SSL authentication is similar to Oracle, but requires no additional properties. However, you can fine tune the connection using parameters described in details in the below document.
See more in PostgreSQL - Configuring the Client.
Kerberos
LDAP
TBD
Encryption types
None
No encryption between database server and the tool enabled. It is not recommended for connections to the production environments.
SSL
You can provide trusted server certificate and make the connection between the database server and the tool secure.
TODO: Add the "How to extract server certificate from Oracle and PostgreSQL" section here.
User Properties
You can define custom JDBC driver properties and pass them directly to the driver.
We do not validate if the properties supported by the driver, and do not recommend to share secrets in the properties section.
Please find additional details on the supported driver properties in the respective JDBC drivers documentation below.
PostgreSQL - Connection to the Database.
Connection Timeout
By default the connection timeout depends on the connection setting.
Secured connections capture global default SSL context and have only 5 seconds to complete, while normal connections timeout is 60 seconds. You can define user property to change the default behavior.
com.epam.tdm.jdbc.connectionTimeout
Test Connection
TBD
Save Connection
TBD